Plus1 Notes Chapter2
(Motion In a Straight Line)
In the above figure if a particle starts moving from A and reaches B through the path AB and then moves towards C through the path BC then
distance travelled = AB+BC but the displacement is AC
Eg Numericals Available(eg 2.1) on page Click Here For Numericals
Graphs
Position-Time graph
A line parallel to x axis(time axis) shows a stationary object
The slope of the position-time graph gives the velocity at that instant
By plotting a position-time graph of two particles in a same graph paper and observing the slopes we can compare the velocity of two particles
Eg Numericals Available(eg 2.7) on page Click Here For Numericals
The slope of A is more than slope of B so the particle A is moving with greater speed
Velocity-Time Graph
In a uniform motion the graph is straight line parallel to the time axis
The area under the curve will give you the displacement
The slope of the graph gives the accelaration at that instant
a=(v-u)/(t2-t1)
Eg Numericals Available(eg 2.6) on page Click Here For Numericals
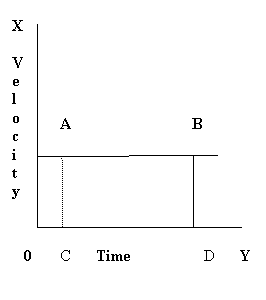
The area under AB will give you the displacement
Area=AB × AC
ie Area=V× t , But it is displacement
Average speed
It is the ratio of the total distance to the total time taken
Average speed= Total Distance / Total time taken
Important Formulas and Notes
Displacement is the change in position in a particular direction in a given interval of time it is independent of the path but depends only on initial and final positions.
It is a vector quantity, it can be either positive,negative or even zero.
Distance is a scalar quantity and it shows the length of the path ie it is path dependent. It can be either zero or positve
Velocity is the rate of change of displacement ie Displacement / time so it is a vector quantity
Velocity=Displacement / time
V=dx/dt
Speed is distance covered by a body in unit time it is scalar quantity
Speed=Distance / time
The dimension of velocity and speed is same and it is M0L1T-1
In the above figure if a particle starts moving from A and reaches B through the path AB and then moves towards C through the path BC then
distance travelled = AB+BC but the displacement is AC
Eg Numericals Available(eg 2.1) on page Click Here For Numericals
Graphs
Position-Time graph
A line parallel to x axis(time axis) shows a stationary object
The slope of the position-time graph gives the velocity at that instant
By plotting a position-time graph of two particles in a same graph paper and observing the slopes we can compare the velocity of two particles
Eg Numericals Available(eg 2.7) on page Click Here For Numericals
The slope of A is more than slope of B so the particle A is moving with greater speed
Velocity-Time Graph
In a uniform motion the graph is straight line parallel to the time axis
The area under the curve will give you the displacement
The slope of the graph gives the accelaration at that instant
a=(v-u)/(t2-t1)
Eg Numericals Available(eg 2.6) on page Click Here For Numericals

The area under AB will give you the displacement
Area=AB × AC
ie Area=V× t , But it is displacement
Average speed
It is the ratio of the total distance to the total time taken
Average speed= Total Distance / Total time taken
If a particle travels with speed of u for for a time interval of t1sec and v for a time interval of t2sec
Average speed=(ut1+ v t2) /( t1+ t2)
Refer eg 2.11 on page Click Here For Numericals
Accelaration
It is the rate of change of velocity
a=Change in velocity / Time
a=d2x/dt2
Important equations of motion
v=u+at
v2=u2+2aS
Sn=u + ½ a(2n-1)
where Sn is the distance covered in the nth second
For free fall replace accelaration a with +g and u with zero
For a body thrown vertically up then in the equation a with -g
For a body thrown vertically up at the maximum height v=0
Relative Velocity
It is the velocity of one body with respect to another body
VA is the velocity of the body A and VB that of body B then the relative velocity of B with respect to A ie VAB , when they are moving in the
same direction(θ=0°) is (VB- VA) and ( VB+ VA) if they are moving in the opposite direction( θ=180°)
The general formula to find the relative velocity is √(VB2+ VA2 - 2VBVAcosθ)
VAB= -VBA
Refer eg 2.5, 2.9, 2.10 on page Click Here For Numericals


Comments
Post a Comment